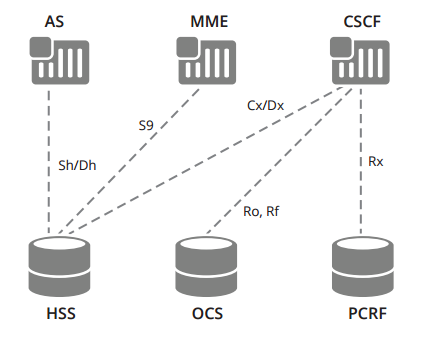
Diameter is a next-generation industry-standard protocol used to exchange authentication, authorization, and accounting (AAA) information in Long-Term Evolution (LTE) and IP Multimedia Systems (IMS) networks. It was derived from, and improves upon, the widely deployed RADIUS (Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service) and LDAP (Lightweight Directory Access Protocol) AAA protocols, providing more reliable, secure, and flexible transport mechanisms for mobile data networks. A variety of LTE and IMS network functions make use of Diameter, including the Policy and Charging Rules Function (PCRF), Home Subscriber Server (HSS), and Online Charging System (OCS) elements. The protocol provides a general framework for exchanging AAA messages and specifies a standard set of AAA request and response commands and attributes. Ribbon offers a Diameter Signalling Controller DSC 8000.
What is Diameter Protocol: Example of Diameter-Based Interfaces in an IMS Network
Relationship to SIP
Diameter and SIP (Session Initiation Protocol) are the core signaling protocols used in IMS networks. SIP is used to establish and control real-time IP communications sessions. Diameter is used to authenticate, authorize and provide accurate billing information for those sessions.
Improvements over RADIUS
RADIUS was conceived to provide basic authentication functions for dial-up networks. In a typical RADIUS implementation, a subscriber provides credentials (i.e. a user ID and password) to an access server upon login. The access server authenticates the credentials against a centralized LDAP policy store. The RADIUS model is not well suited for IMS networks where mobile users access a variety of dynamic applications and services across autonomous service provider networks.
Diameter supports the enhanced policy control, dynamic rules, quality of service, bandwidth allocation and charging mechanisms needed for contemporary communications service provider networks. It also provides a more reliable, secure and flexible framework for exchanging AAA messages.
Diameter Protocol Advantages:
- A peer-to-peer architecture for greater flexibility
- Reliable transmission of AAA messages over TCP or SCTP
- Built-in failover mechanisms to guarantee message delivery
- Secure transmission of AAA messages using TLS or IPSec
Peer-to-Peer Architecture
Diameter is based on a peer-to-peer architecture. The protocol defines three distinct types of nodes: client, server, and agent. The diameter node that receives the user connection request (i.e. a network access server) is referred to as the client. The diameter node that processes the request is referred to as the server. Intermediary nodes are referred to as agents. The protocol defines four distinct agent types: proxy, redirect, relay, and translation.
Diameter Protocol Agents Functionality:
- Provide load balancing for scalability and reliability
- Perform value-added request or response processing
- Aggregate, concentrate, sort, and forward requests
- Enable interworking with legacy AAA protocols
- Mitigate multivendor interoperability issues
Diameter Signaling Controllers
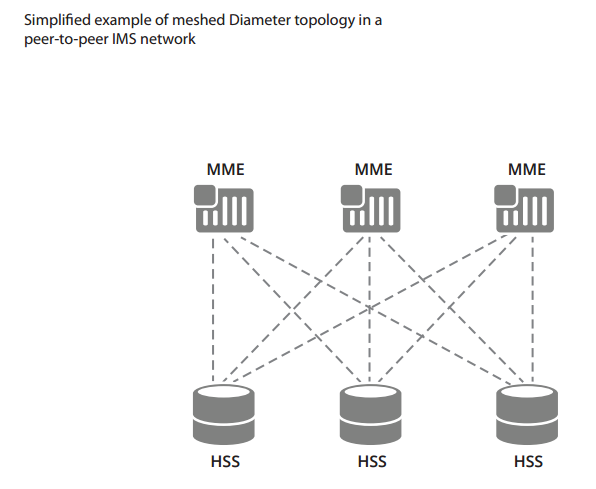
Peer-to-peer communications flow results in a mesh topology (often referred to as an “N-squared” connected mesh) which is inherently difficult to scale and manage. (See figure below.)
A Diameter Signaling Controller (DSC) provides intermediary routing and protocol mediation functions allowing service providers to collapse complex Diameter mesh topologies into simpler, hierarchical hub-and-spoke topologies that are more scalable and more easily managed. (See figure below).
.jpg)