SIP (Session Initiation Protocol) has emerged as the signaling protocol of choice for Voice over IP (VoIP) and unified communications (UC). The popular protocol is supported in a wide variety of contemporary IP communications products including IP-PBXs, unified communications servers, applications servers and videoconferencing systems as well as a range of endpoints. Many communications service providers now offer SIP trunking services as flexible, cost-effective alternatives to conventional PRI (Primary Rate Interface) trunks.
What is SIP Trunking: Applications
SIP Trunking is employable in a variety of applications, including:
- PSTN origination/termination – to connect businesses to the PSTN
- Site-to-site connectivity – to interconnect geographically distributed business locations
- Cloud or hosted service connectivity – to connect businesses to remotely hosted communications services such as voice or video conferencing services
SIP Trunking Benefits
There are a variety of SIP Trunking benefits compared to traditional PRI trunks, including:
- Lower circuit costs – SIP trunks support greater call densities than PRIs. While a T1 PRI supports only 23 concurrent calls, a TI-based SIP trunk can support 50 or more concurrent calls without impacting call quality.
- Better service agility – SIP trunking services can be turned up much more quickly than conventional PRI circuits. In addition, many service providers support bursting options, allowing customers to temporarily add capacity to accommodate traffic surges.
- Lower PSTN origination/termination fees – SIP trunking providers generally offer lower international calling rates and simpler (flat) pricing structures.
Enterprise SIP Trunking Architectures
Multi-site enterprises can implement SIP trunks in a distributed or centralized fashion (or a hybrid of the two). In the distributed architecture each enterprise site connects to the PSTN via distinct SIP trunks. In the centralized architecture, SIP trunks are installed in centralized data centers and remote sites are connected over the corporate IP data network (see figure below).
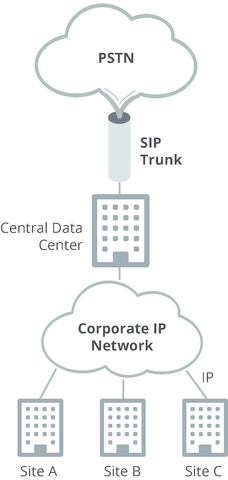
The centralized architecture offers a number of benefits, including:
- Lower trunking fees – enterprises can reduce expenses by consolidating trunks into centralized data centers
- Contact center take back and transfer fee elimination – businesses can eliminate expensive service provider take back and transfer fees by interconnecting distributed contact centers over the corporate IP data network
- Toll bypass – enterprises can avoid PSTN charges by carrying site-to-site calls over the corporate IP data network
Role of Enterprise Session Border Controllers in SIP trunking
An Enterprise Session Border Controller (E-SBC) is a special-purpose device that mitigates SIP security, interoperability and interworking challenges. E-SBCs are typically installed at the edge of an enterprise network as the demarcation point for a SIP trunking service. Some SIP trunking service providers bundle customer premises-based E-SBCs with the service, maintaining ownership and management of the device. Some providers implement the E-SBC in the service provider network as a virtual appliance. Still other SIP trunking service providers recommend customers purchase and manage their own E-SBCs.

