Voice over LTE, VoLTE is a way that operators can transfer traffic for voice over LTE in a standardized manner. In the beginning, LTE was only used for data transfer, and systems such as 2G / 3G were used to carry voice over existing networks. But that method proved to create incompatibility issues for most phones that lacked the ability to communicate with one another. VoLTE is based on the IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS) network. This method allows voice service to take the form of data flows within the LTE data bearer as it is being delivered. The result of this is that there is no need for a legacy circuit switch network, and allows for more voice and data capacity than that of a 2G and 3G network. VoLTE supports packet switching and works primarily on an IP-based network. It receives data from a cellular network via a circuit switch such as the Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM) or a Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA) network to be converted into packets that the network will then broadcast. As with any digital voice system, a codec is used. 3GPP is the adaptive multi-rate (AMR) codec used by VoLTE, and in some cases, the AMR-wideband codec may also be used. The AMR codec is used by many cellular systems as it provides an advantage in terms of interoperability with legacy systems.
Simplified VoLTE SRVCC Architecture
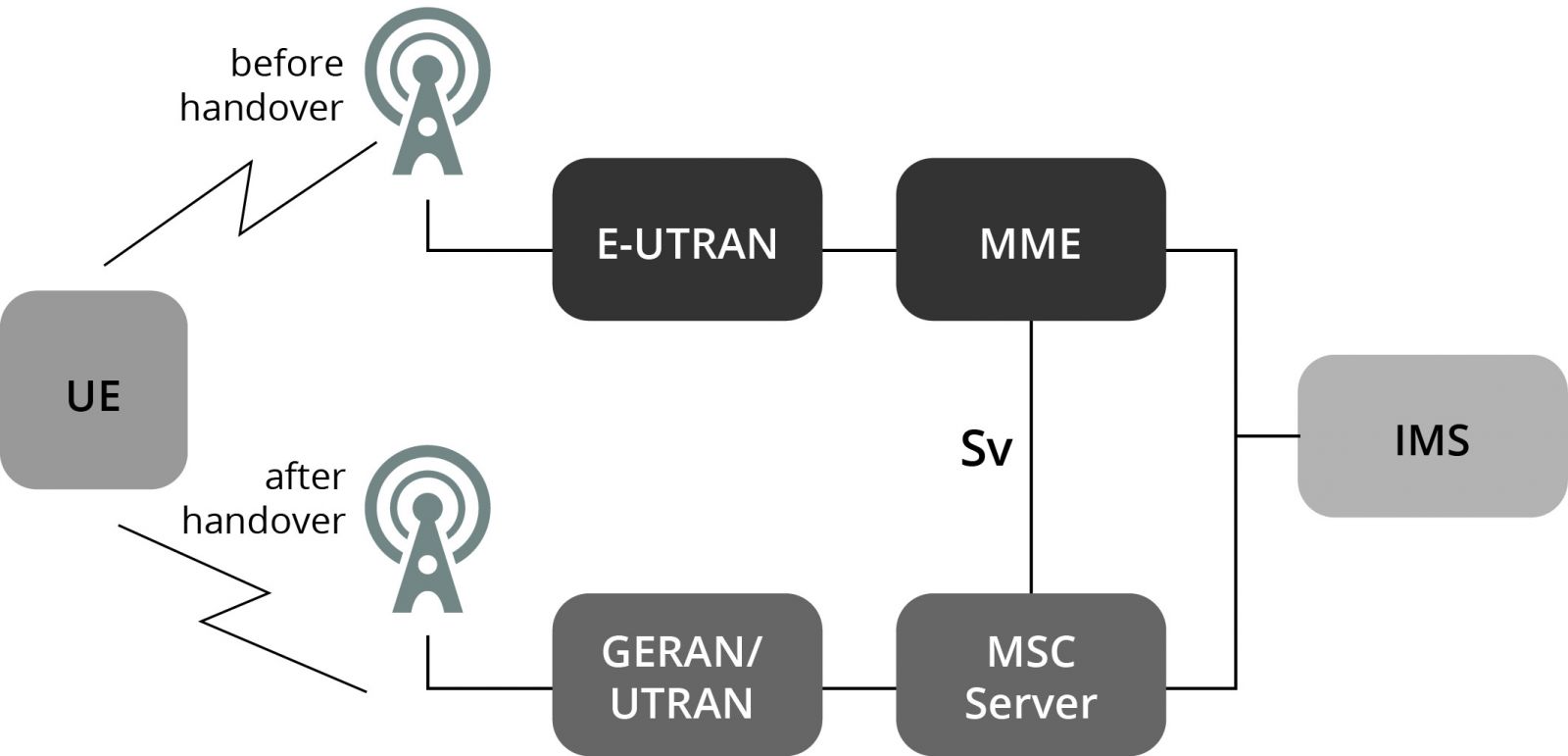
- IMS - IP Multimedia Subsystem
- MME - Mobility Management Entity
- MSC Server - Mobile Switching Centre Server
- E-UTRAN - Evolved Universal Terrestrial Radio Access Network
- GERAN - GSM/EDGE Radio Access Network
- UTRAN - Universal Terrestrial Radio Access Network
- UE - User Equipment

