In service provider networks a signaling gateway is a translation device that is used to pass call control information between dissimilar networks such as legacy SS7 (signaling system 7) networks and IP-based networks. A signaling gateway can be implemented as a standalone network element or embedded into a network element such as a media gateway controller/softswitch. Signaling gateways enable service providers to gradually expand and modernize their networks while protecting and extending previous investments and maintaining support for legacy services and regulatory requirements.
The Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) signaling transport working group (SIGTRAN) introduced the concept of a signaling gateway in RFC 2719, a Framework Architecture for Signaling Transport, as a way to translate SS7 signaling to IP signaling. Signaling gateways are also used to interwork VoIP or IP multimedia communications networks that employ different signaling protocols such as SIP (session initiation protocol) and H.323.
What is a Signaling Gateway: Service Provider Applications
Service providers use signaling gateways to interwork disparate wireless, wireline, access, core, TDM and IP networks. Originally employed by service providers as part of next-generation IP network initiatives, signaling gateways are now used in a wide variety of applications.
Fixed line and mobile service providers use signaling gateways to:
- Interwork GSM, UMTS, CDMA, and satellite networks in 2G, 3G, and 4G/LTE architectures
- Provide Class 4/IP Tandem/IP Trunking and Class 5/subscriber interworking for fixed networks
- Deliver SIP-based services to legacy TDM-based customers
- Replace legacy TDM central office switches
- Perform IP-to-IP signaling conversion (i.e. SIP to H.323) in heterogeneous IP networks
The figure below depicts a signaling gateway in a classic offload application where a service provider backhauls PSTN traffic over a more cost-effective IP network.
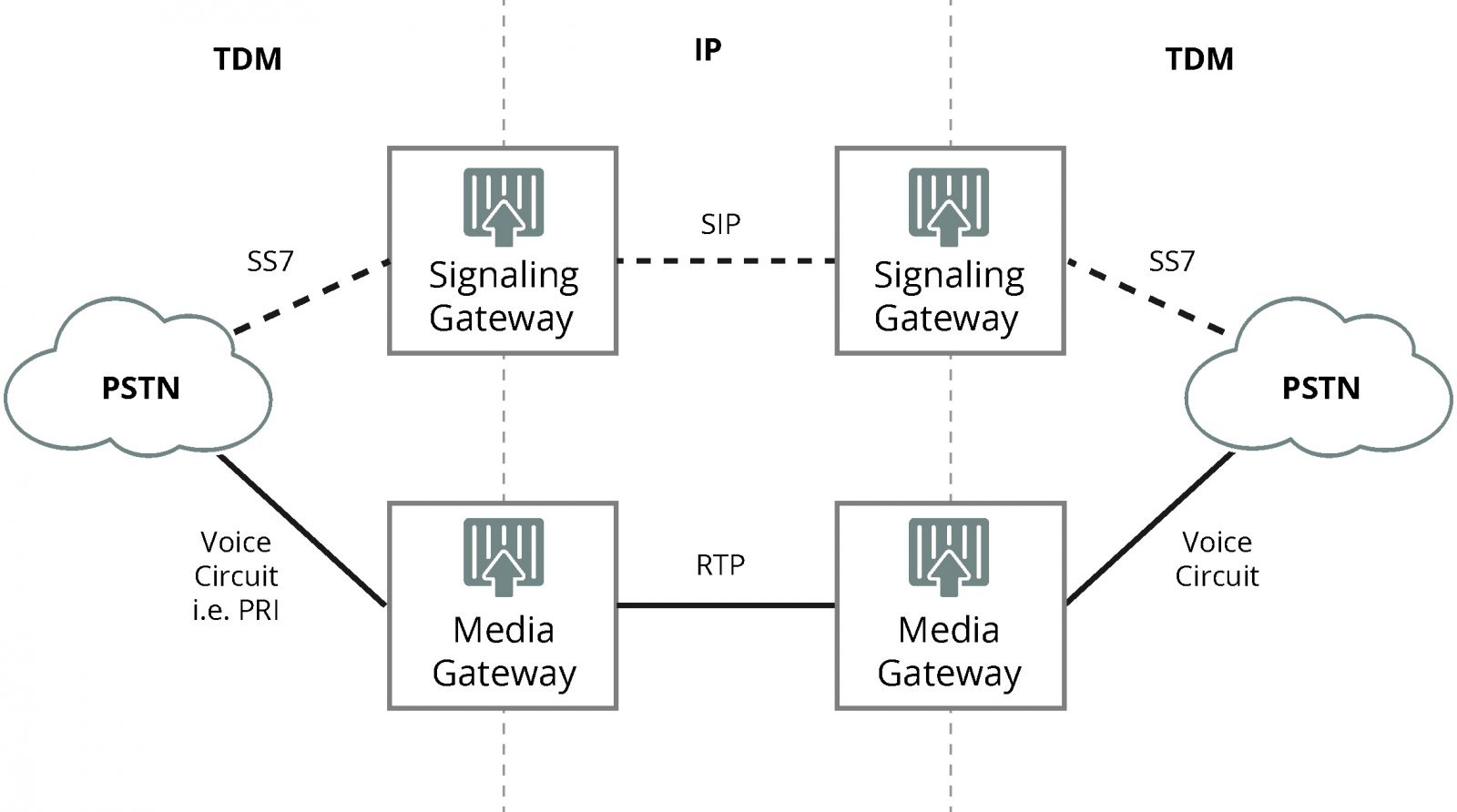
Relationship to Media Gateways
Signaling gateways are employed in conjunction with media gateways. In SS7/IP applications, the media gateway terminates PSTN circuits and packetizes the media streams for IP transport using protocols such as RTP (real-time transport protocol) or SRTP (secure RTP). Some vendors offer integrated signaling/media gateway solutions.

