A Session Border Controller or SBC is a special-purpose device that protects and regulates IP communications flows. As the name implies, session border controllers are deployed at network borders to control IP communications sessions. Originally conceived to protect and control VoIP networks, SBCs are now used to regulate all forms of real-time communications including VoIP, IP video, text chat and collaboration sessions.
Download SBC for Dummies Guide
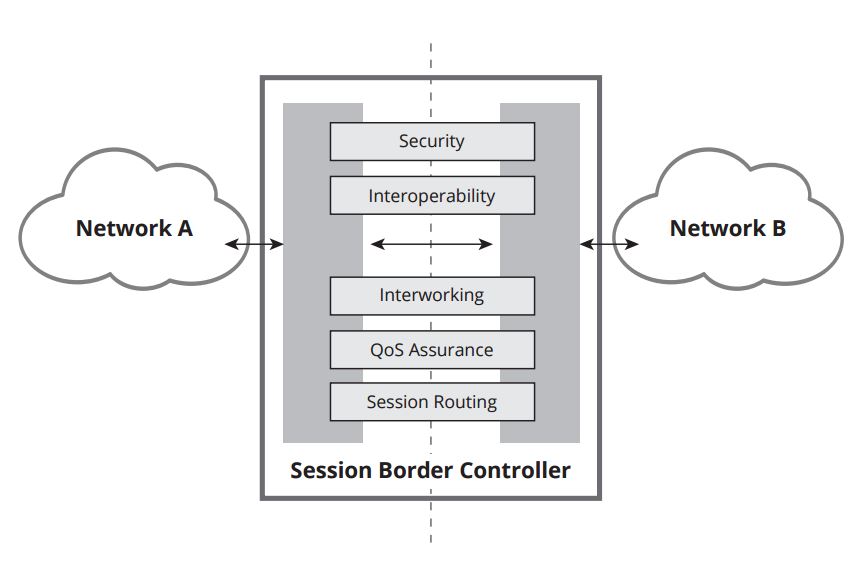
What is a Session Border Controller: Functions
- Security - SBCs protect against Denial of Service (DoS) and Distributed DoS (DDoS) attacks, safeguard against toll fraud and service theft, and provide media and signaling encryption to ensure confidentiality and protect against impersonation/masquerade
- Multivendor interoperability - SBCs normalize SIP (Session Initiation Protocol) signaling stream headers and messages to mitigate multivendor incompatibilities
- Protocol interworking - SBCs enable interworking between diverse protocols (i.e. SIP-to-H.323) or diverse codecs (i.e. g.711 to g.729 transcoding)
- Quality of service (QoS) - SBCs enforce call admission control (CAC) policies, type of service (ToS) marking, or rate limiting for service quality assurance
- Session routing - SBCs route sessions across network interfaces to ensure high availability or enable least cost routing (LCR)
Session Border Controller Types
Communications service providers and enterprises both make use of SBCs. Service providers deploy SBCs at access, core and interconnect network borders. Enterprises typically deploy SBCs at the edge of the enterprise network, for example as the termination point for a SIP trunking service. Because of the diverse functional and scalability requirements many manufacturers offer distinct service provider SBC and enterprise SBC product families. Enterprise SBCs are commonly referred to as E-SBCs or eSBCs. Some SBC manufacturers offer software-based SBCs that run on virtualized industry-standard servers to enable network functions virtualization (NFV).
Download SBC for Dummies Guide
Session Border Controller Applications
- SIP trunking – Enterprise Session Border Controllers (E-SBCs) are typically installed at the edge of an enterprise network as the demarcation point for a SIP trunking service. Some SIP trunking service providers bundle customer premises-based E-SBCs with the service, maintaining ownership and management of the device. Some providers implement the E-SBC in the service provider network as a virtual appliance. Still other SIP trunking service providers recommend customers purchase and manage their own E-SBCs.
- IP contact centers – E-SBCs are often deployed at corporate IP network borders to route calls across distributed IP contact center environments. Many organizations are migrating legacy TDM-based contact center networks to all-IP networks to eliminate expensive PSTN “take back and transfer” fees.
- Cloud-based IP communications services – E-SBCs are used to protect and control access to remotely hosted or cloud-based IP communications services such as audio or video conferencing services.
- Mobile workers and small offices – E-SBCs are installed at Internet borders to securely extend corporate IP communications services to small offices, mobile workers or teleworkers.
- Unifying disparate communications environments – E-SBCs are often used to transform fragmented communications environments composed of distinct PBX or UC implementations into integrated systems with unified dial plans, features and policies.
- Service provider border security – Service providers use SBCs to protect and control core network borders, access network borders (customer-facing services) and interconnect borders (connections to other service provider networks and legacy networks)