Learn about CWDM vs DWDM
CWDM vs DWDM: What is the Difference & Which Should You Use
Meeting bandwidth capacity needs of customers is a crucial business objective for today’s providers. While both coarse wavelength-division multiplexing (CWDM) and dense wavelength-division multiplexing (DWDM) are modern forms of wavelength-division multiplexing (WDM) that effectively solve those increasing bandwidth needs by upgrading the utilization of new and existing fiber, they are each designed to tackle different network challenges.
CWDM and DWDM have different wavelength set ups and applications—and by understanding how they work and how they differ, providers can make more informed decisions around which technology may be best when planning a network.
Here, we’ll take a deep dive into CWDM and DWDM, including key qualities of each, their major differences, and how to go about choosing the right technology.
CWDM
CWDM is a system designed for shorter-range communications, using a few wavelengths spread far apart. It’s an economical technology that can be deployed on most types of fiber networks, well suited for point-to-point topologies in enterprise and telecom access networks with moderate data transmission needs.
DWDM
DWDM technology uses tighter wavelength spacing to fit more channels onto a single fiber. It supports 96 channels spaced at 0.8 nm apart within the 1550 nm C-Band spectrum. Tighter wavelength spacing accommodates more channels, which enables large amounts of data to be transmitted across a single cable.
This technology is often used for interconnecting data centers and financial services networks, for telecom metro networks where it is deployed in a ring topology, and for long distance networks. A DWDM wavelength channel can move up to 800 gigabits of data per second, and multiple wavelengths can combine to move over 25 terabits of data per second on a single fiber. Because of these capabilities, DWDM works better for high capacity applications.
What is the difference between CWDM and DWDM?
While CWDM and DWDM are both used to transmit a mix of data across a single fiber on various channels, the two technologies vary in several ways:
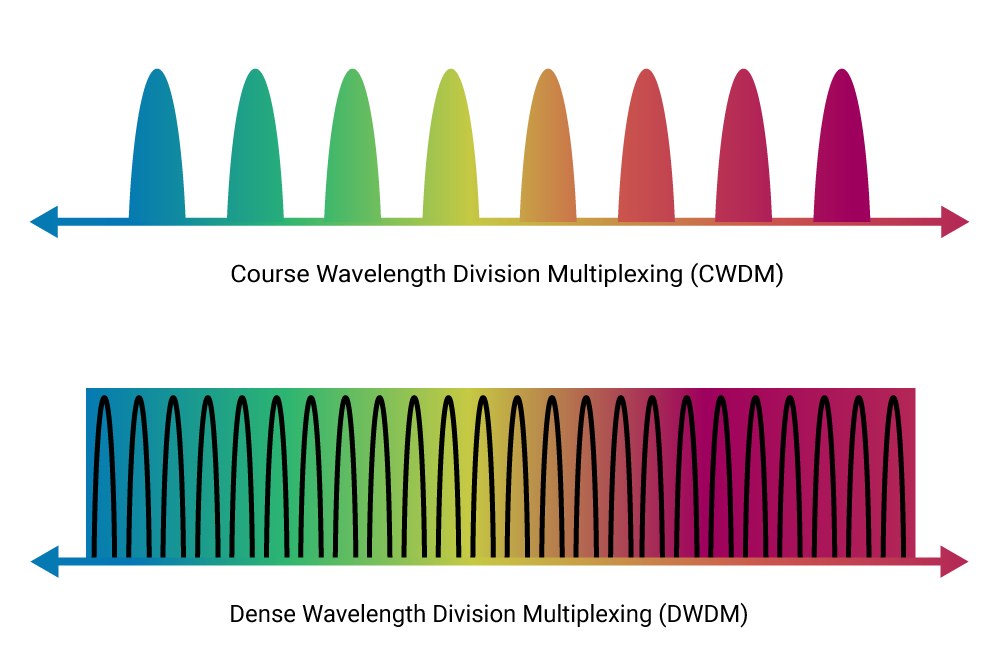
Channel spacing
Wavelength spacing impacts the channel capacity of each technology. CWDM has wider spacing and can transport eight wavelengths with a 20 nm channel spacing in the C-band spectrum. DWDM systems not only support more channels, but also can be boosted using optical amplifiers to transmit data over longer distances. That’s because they use narrower channel spacing of 0.8/0.4 nm to carry 40, 80, 90, 96, or even 160 wavelengths.
Transmission distance
As mentioned before, CWDM is not suitable for long-haul transmission, as its maximum has been found to be around 160 km. DWDM, on the other hand, transmits data across much longer distances for up to thousands of kilometers because its wavelengths can be amplified within the fiber during light transmission, allowing for a longer reach.
Traditionally, DWDM has been more expensive compared to CWDM because of the more demanding technical requirements for their laser transmitters and optical receivers. More recently, the growing popularity of DWDM and technology advances has started to close this price gap.
Because these two major subsets of WDM offer different features, providers should weigh out which technology might be best for their organization. Beyond their nuances, it’s important to evaluate how each would impact the business and end-customers before deploying either technology.
Cost
Traditionally, DWDM has been more expensive compared to CWDM because of the more demanding technical requirements for their laser transmitters and optical receivers. More recently, the growing popularity of DWDM and technology advances has started to close this price gap. Because these two major subsets of WDM offer different features, providers should weigh out which technology might be best for their organization. Beyond their nuances, it’s important to evaluate how each would impact the business and end-customers before deploying either technology. Multiple technologies are capable of moving data quickly and efficiently across a network. Watch our webinar to learn the challenges, features, benefits of the options out there.
CWDM or DWDM - Which Should You Choose?
Though the actual and projected growth of DWDM continues to rise, both CWDM and DWDM are viable options when trying to solve customers' growing bandwidth needs.
Some providers gravitate toward CWDM technology because it’s well-suited for their short-range applications. If they don’t require great range, significantly large capacity, or the ability to increase that capacity in the future, CWDM might be the right fit. This technology offers smaller, more cost-effective wave filters, and enables the use of SMF fiber or MMF cable—which provides a bit more flexibility.
DWDM, on the other hand, offers greater distance and capacity. It also offers a cost-effective “pay-as-you-grow” model. It’s suitable for long-haul transmissions, can be used with existing fiber optic cables, and is also protocol and bitrate independent; all of which makes DWDM an attractive option for providers who offer multiple services to their customers, for example a cable TV-phone-Internet package.
In fact, organizations spanning many industries are now leaning more towards DWDM. Dell'Oro predicts that the DWDM market will grow approximately 3% to $18 billion by 2026. Providers looking to future-proof their solutions look to DWDM to align with their unique business needs, while garnering strong ROI and better meeting their customers’ needs.
A Competitive Network Solution with Ribbon
When planning a network, both CWDM and DWDM will allow you to meet your customers’ increasing bandwidth capacity needs, however, both solutions have different wavelength patterns and applications. Finding a solution that meets current and future needs requires you to understand how each of these technologies work as well as their limitations.
Ribbon helps organizations modernize their networks for improved competitive positioning and business outcomes in today’s data-hungry world.
Ribbon’s IP Wave is a purpose-built framework of service-driven IP optical networking solutions that enable service providers, enterprises, and critical infrastructure companies to address major network and operational challenges. They build, deploy, manage, and help future-proof multi-layer data and optical networks and customize it to your organization’s needs.





