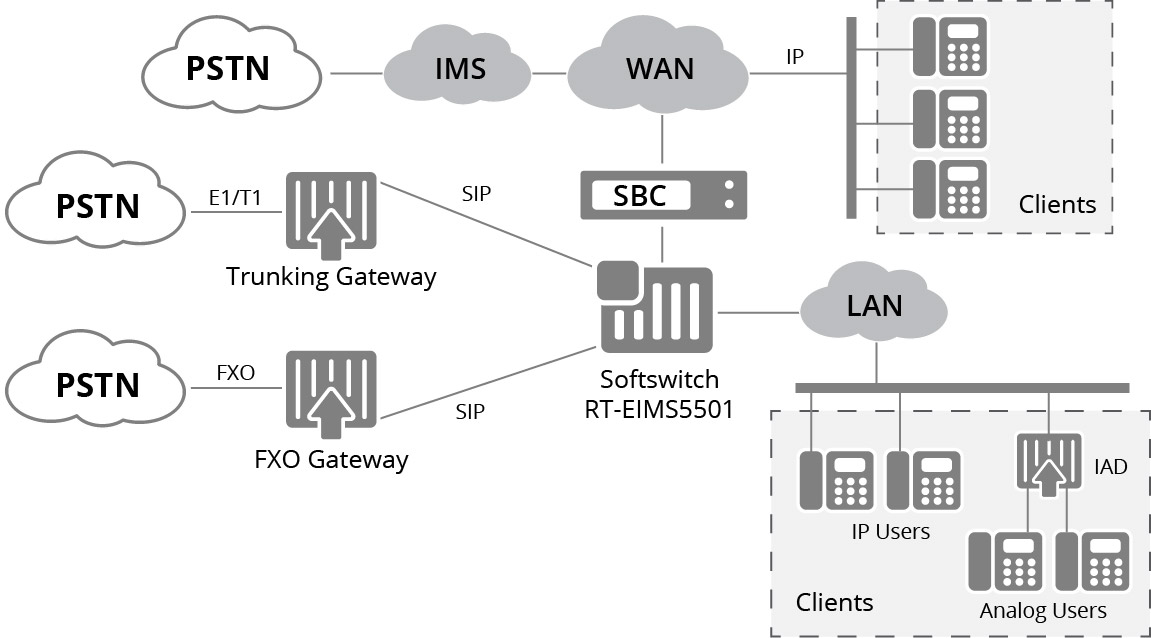
In today's market, most networks are comprised of a variety of combinations of telephony switches and hardware. One of those elements is a softswitch, which also acts as a VoIP server allowing for telecommunication networks to provide management of voice, fax, data and video traffic, and call routing. VoIP softswitches can be subdivided into class 4 and class 5 softswitches.
Class 4 Softswitch vs Class 5 Softswitch
Class 4 VoIP softswitches are used to route calls between carriers or over long distances. For example, in a VoIP trunking application the Class 4 switch sits at the intersection of the local PSTN network and the long-haul IP backbone network. Class 5 VoIP softswitch is intended to provide services to the end users of companies such as residential or business clients. Class 5 softswitches are used in the access network, for example to interface TDM access lines to a local carrier’s VoIP network.